
Many people are confused about how diamonds are priced. The best explanation is that asking for the price of a diamond is like asking for the price of a house. A real estate agent can't quote you a price for a house without knowing its size, condition, location, etc. This process is similar to the one used to quote the price of a diamond.
The 4C'S

A diamond's beauty, rarity, and price depend on the interplay of all the 4Cs-cut, clarity, carat, and color. The 4Cs are used throughout the world to classify the rarity of diamonds. Diamonds with the combination of the highest 4C ratings are more rare and, consequently, more expensive. No one C is more important than another in terms of beauty and it is important to note that each of the 4Cs will not diminish in value over time.
Clarity
Refers to the presence of inclusions in a diamond. Inclusions are natural identifying characteristics such as minerals or fractures, appearing while diamonds are formed in the earth. They may look like tiny crystals, clouds or feathers. To view inclusions, jewelers use a magnifying loupe. This tool allows jewelers to see a diamond at 10x its actual size so that inclusions are easier to see. The position of inclusions can affect the value of a diamond. There are very few flawless diamonds found in nature, thus these diamonds are much more valuable. Inclusions are ranked on a scale of perfection, known as clarity, which was established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA).
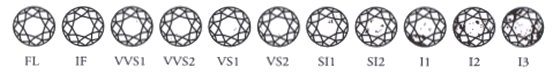
The clarity scale, ranging from F (Flawless) to I3 (Included), is based on the visibility of inclusions at a magnification of 10x. Some inclusions can be hidden by a mounting, thus having little effect on the perceived beauty of a diamond. An inclusion in the middle or top of a diamond could impact the dispersion of light, sometimes making the diamond less brilliant. The greater a diamond's clarity, the more brilliant, valuable and rare it is-and the higher it is on the Diamond Quality Pyramid, the more the diamond will cost. At WeddingBands.com all the diamonds that we are using in the Diamond Wedding Bands are at least VS2 in clarity.
Color
Refers to the degree to which a diamond is colorless. Diamonds range in color from icy winter whites to warm summer whites. Diamonds are graded on a color scale established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) which ranges from D (colorless) to Z. Warmer colored diamonds (K-Z) are particularly desirable when set in yellow gold. Icy winter whites (D-J) look stunning set in white gold or platinum. Diamonds that fall below J will have a faint yellow tint that can be clearly seen. The lower down the diamond color scale the more color will be visible and less expensive. This color is not to be confused with the Z+ category. The Z+ category is for fancy colored diamonds, such as fancy yellow diamonds.

Color differences are very subtle and it is very difficult to see the difference between, say, an E and an F. Therefore, colors are graded under controlled lighting conditions and are compared to a master set for accuracy. Truly colorless stones, graded D, treasured for their rarity, are highest on the Diamond Quality Pyramid. Color, however, ultimately comes down to personal taste. At Wedding Bands .com all the diamonds we are using in our Diamond Wedding Rings are at least H in color.
Cut
Refers to the angles and proportions of a diamond. Based on scientific formulas, a well-cut diamond will internally reflect light from one mirror-like facet to another, disperse, and reflect it through the top of the stone. This results in a display of brilliance and fire, thereby placing well-cut diamonds higher on the Diamond Quality Pyramid than deep or shallow-cut diamonds. Diamonds that are cut too deep or too shallow lose or leak light through the side or bottom, resulting in less brilliance and ultimately, value. At Wedding Bands .com the diamonds we use in our Diamond Wedding Rings are all very fine cut to show the maximum brilliancy and fire.
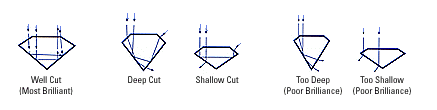
Cut also refers to shape-round, square, pear, or heart for example. Since a round diamond is symmetrical and capable of reflecting nearly all the light that enters, it is the most brilliant of all diamond shapes and follows specific proportional guidelines. Ask a jeweler to find out more about these guidelines. Non-round shapes, also known as "fancy shapes," will have their own guidelines to be considered well-cut.
What to Spend
Diamond Buyer's Guide When you start to think about buying a diamond-and the love it will symbolize-you naturally want the best you can afford and a beautiful stone you will treasure forever. Diamonds can be found in a broad range of prices-and you're certain to find one within the Diamond Quality Pyramid that suits your taste and what you plan to spend. If you are about to buy a Diamond Engagement Ring, you may want to consider spending the commonly accepted guideline of two months salary. But it's up to you to settle on a diamond that will truly represent your deepest emotions and the promise for the future you will share.
At WeddingBands.com no purchase is complete until you are satisfied.
Information
Policies
© Copyright
1995-2025 WeddingBands.com. All rights reserved
